MercoPress. South Atlantic News Agency
Tag: Climate change
-
Monday, August 17th 2020 - 09:57 UTC
Climate change could trigger epidemics: malaria, dengue, zika, smallpox and pathogens from Siberian permafrost

The COVID-19 pandemic that has swept the globe and claimed more than 760,000 lives so far almost certainly came from a wild bat, highlighting the danger of humanity's constant encroachment on the planet's dwindling wild spaces.
-
Monday, August 3rd 2020 - 10:00 UTC
Lawsuit against Australia for failing to disclose climate-change risks to its sovereign bond purchasers

A 23-year-old student has filed a lawsuit against Australia's government alleging it has failed to disclose climate change-related risks to investors in the country's sovereign bonds, in the first such action against the Australian government.
-
Monday, July 27th 2020 - 09:32 UTC
Argentina ready to launch satellite to monitor logging of native forests mainly in Chaco

Argentina plans to put into orbit a satellite with new precision technology sometime this week, to monitor the felling of its native forests round the clock and accurately measure forest carbon stocks in a bid to help curb climate change, scientists said.
-
Tuesday, July 21st 2020 - 08:44 UTC
Climate change starving polar bears to extinction, according to latest report

Climate change is starving polar bears into extinction, according to research published on Monday that predicts the apex carnivores could all but disappear within the span of a human lifetime.
-
Thursday, July 16th 2020 - 07:40 UTC
Report on per capita carbon “food prints” criticizes beef and dairy consumption

If everyone alive ate steaks and dairy the way Brazilians and Americans do, we would need an extra five planets to feed the world, according to the first report to compare the carbon emissions from food consumption in Group of Twenty (G20) nations, released on Thursday.
-
Friday, July 3rd 2020 - 09:19 UTC
IAATO's new guidance to enhance environmentally responsible travel to Antarctica

IAATO, which celebrates its 30th year in 2021, has been carefully monitoring, analyzing, and reporting Antarctic tourism trends since its inception as part of its commitment to the effective self-management of guest activities.
-
Tuesday, June 30th 2020 - 09:49 UTC
South Pole warming at three times the global rate over the last three decades

At the South Pole, considered the coldest point on Earth, temperatures are rising fast. So fast, in fact, that Kyle Clem and other climate researchers began to worry and wonder whether human-driven climate change was playing a bigger role than expected in Antarctica.
-
Monday, June 29th 2020 - 18:32 UTC
Sea ice in the Weddell Sea has decreased by one million sq kilometers in five years
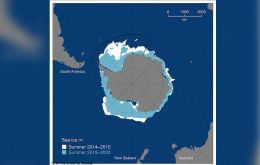
Scientists have discovered that summer sea ice (*) in the Weddell Sea area of Antarctica has decreased by one million square kilometres – an area twice the size of Spain – in the last five years, with implications for the marine ecosystem. The findings are published this month in the journal Geophysical Research Letters.
-
Friday, June 26th 2020 - 08:19 UTC
District of Columbia files lawsuit against oil majors for “misleading” consumers con climate change

The attorney general for the District of Columbia on Thursday filed a lawsuit against Exxon Mobil, BP, Chevron and Royal Dutch Shell for “systematically and intentionally misleading” consumers about the role their products play in causing climate change, the latest action by a US attorney general against the oil and gas industry.
-
Thursday, June 25th 2020 - 05:55 UTC
Micro plastics pollution reaches Antarctica: found in land based food systems

Scientists have found bits of polystyrene in the guts of tiny, soil-dwelling organisms in the Antarctic, raising concern that micro-plastics pollution has already “deeply” entered the world's most remote land-based food systems.
