MercoPress. South Atlantic News Agency
Tierra del Fuego ozone alert with 'UV radiation reaching extreme risk or harm'
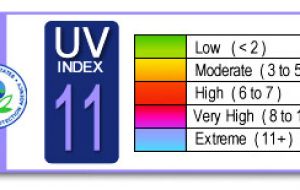 According to the UV Index, a reading of 11 or more means extreme risk of harm from unprotected sun exposure several precautions must be taken
According to the UV Index, a reading of 11 or more means extreme risk of harm from unprotected sun exposure several precautions must be taken 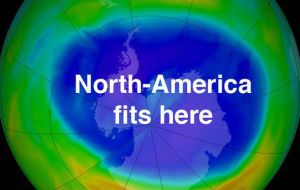 The hole in the ozone layer over Antarctica is now larger than the North American continent.
The hole in the ozone layer over Antarctica is now larger than the North American continent.  Based on data collected in October, it is now measures around 10 million sq miles, which is only slightly smaller than the 2006 record: 10.42m square miles
Based on data collected in October, it is now measures around 10 million sq miles, which is only slightly smaller than the 2006 record: 10.42m square miles Tierra del Fuego in south Argentina has sent out a warning to residents in the province that the ozone layer hole as it expands to the north, over the tip of South America continent this week, it will be reaching its maximum size with UV radiation at 12, violet or extreme alert. The information was provided by Argentina's VAG Ushuaia Station.
According to the international UV Index reading of 11 or more means extreme risk of harm from unprotected sun exposure and several precautions must be taken since unprotected skin and eyes can burn in minutes.
Among which are: Try to avoid sun exposure between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. If outdoors, seek shade and wear protective clothing, a wide-brimmed hat, and UV-blocking sunglasses. Generously apply broad spectrum SPF 30+ sunscreen every 2 hours, even on cloudy days, and after swimming or sweating. Watch out for bright surfaces, like sand, water and snow, which reflect UV and increase exposure.
The hole in the ozone layer over Antarctica is now larger than the North American continent. Based on data collected in October, scientists have announced that it now measures around 10 million square miles, which is only slightly smaller than the record set in 2006, when its size reached 10.42 million square miles across.
The ozone hole, or the ozone depletion phenomenon, is an area in the Earth's stratosphere where the gas that blocks the sun's ultraviolet radiation is depleted below a threshold. Recent legislation and regulations passed across the globe that ban and restrict the use of ozone-depleting chemicals have contributed to the improvement in the ozone situation.
As a matter of fact, the hole over Antarctica is slowly repairing itself, according to several scientific papers, but it's a slow long term process.
The size of the ozone hole, however, varies according to the season, and it tends to grow bigger during the spring and summer. It is currently spring in Antarctica. Scientists from the German Aerospace Center believe that this is caused by the concentration of chlorofluorocarbons, or nontoxic, nonflammable chemicals containing carbon, chlorine and fluorine, which increases because of lower temperatures at this time of the year.
This is thought to contribute in the unusually warm air currents that head towards the South Pole, which deplete the ozone.
The VAG Ushuaia station is located in the Ushuaia peninsula and keeps track of UV radiation and monitors the displacement of the polar vortex. Likewise the station also sends balloons with ozone and meteorological sensors to obtain profiles of the gas and weather conditions associated with its distribution.




Top Comments
Disclaimer & comment rules-

Read all commentsVisit Ushaia and get skin cancer and cataracts. Do the tourist board advertise this as an “extra” ?
Nov 18th, 2015 - 09:57 pm 0Commenting for this story is now closed.
If you have a Facebook account, become a fan and comment on our Facebook Page!