MercoPress. South Atlantic News Agency
Tag: World Health Organization (WHO)
-
Saturday, May 2nd 2015 - 10:46 UTC
“World closer than ever to wipe out polio, but no victory declaration yet”

The world is closer than ever to being able to wipe out polio, international experts said, with zero cases of the crippling disease recorded across all of Africa this year and fewer than 25 globally.
-
Thursday, April 30th 2015 - 10:08 UTC
Only 34 countries with plans to fight threat of antibiotic resistance, says WHO

Only 34 countries have national plans to fight the global threat of antibiotic resistance, meaning few are prepared to tackle “superbug” infections which put even basic healthcare at risk, the WHO has said. In a survey of government plans to tackle the issue, the World Health Organization said only a quarter of the 133 countries that responded were addressing the problem.
-
Monday, April 27th 2015 - 21:57 UTC
WHO calls for renewed efforts in global vaccination targets for 2015
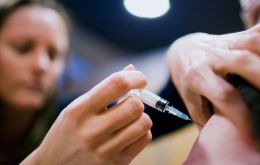
Progress towards global vaccination targets for 2015 is far off track with 1 in 5 children still missing out on routine life-saving immunizations that could avert 1.5 million deaths each year from preventable diseases. In the lead-up to World Immunization Week 2015 (24 -30 April), the World Health Organization (WHO) is calling for renewed efforts to get progress back on course.
-
Thursday, March 5th 2015 - 11:05 UTC
WHO calls on countries to reduce sugars intake among adults and children

A new WHO guideline recommends adults and children reduce their daily intake of free sugars to less than 10% of their total energy intake. A further reduction to below 5% or roughly 25 grams (6 teaspoons) per day would provide additional health benefits.
-
Tuesday, January 20th 2015 - 05:57 UTC
WHO calls for urgent action to reduce burden of non communicable diseases

Urgent government action is needed to meet global targets to reduce the burden of non-communicable diseases (NCDs), and prevent the annual toll of 16 million people dying prematurely—before the age of 70 – from heart and lung diseases, stroke, cancer and diabetes, according to a new World Health Organization report.
-
Wednesday, January 14th 2015 - 07:01 UTC
Cancer 'bad luck' theory strongly questioned by WHO specialized agency
The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), the World Health Organization’s specialized cancer agency, strongly disagrees with the conclusion of a scientific report on the causes of human cancer published in the journal Science on 2 January 2015 by D. Christian Tomasetti and Dr. Bert Vogelstein.
-
Friday, November 28th 2014 - 06:08 UTC
World health experts meet to discuss the high levels of antibiotic resistance

Next week, 2-3 December, senior government representatives from more than 30 countries are expected to agree on a pilot system for collecting data on antibiotic resistance—a major step forward in addressing this threat to global public health.
-
Tuesday, November 11th 2014 - 07:12 UTC
”Ageing well”, says WHO: in 2020 over 60 will outnumber children under 5

A major new Series on health and ageing, published in “The Lancet”, warns that unless health systems find effective strategies to address the problems faced by an ageing world population, the growing burden of chronic disease will greatly affect the quality of life of older people.
-
Friday, October 24th 2014 - 20:17 UTC
France reports four cases of chikungunya locally acquired infections

On 21 October 2014, WHO was notified by the National IHR Focal Point for France of 4 cases of chikungunya locally-acquired infection in Montpellier, France. The cases were confirmed by tests conducted by the French National Reference Laboratory for arboviruses on 20 October 2014. This is the first time that locally-acquired transmission of chikungunya has been detected in France since 2010.
-
Monday, October 20th 2014 - 07:30 UTC
WHO admits full-scale battle with tobacco industry, which appeals to 'devious channels'

The sixth session of the Conference of the parties (COP6) to the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (FCTC) concluded in Moscow. Several landmark decisions were adopted in the course of the six-day session, regarded as one of the most successful in the WHO FCTC’s history.
