MercoPress. South Atlantic News Agency
Tag: World Health Organization (WHO)
-
Saturday, May 21st 2022 - 07:49 UTC
WHO working closely with (ten) countries responding to monkey-pox
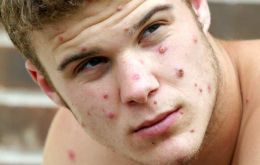
WHO and partners are working to better understand the extent and cause of an outbreak of monkeypox. The virus is endemic in some animal populations in a number of countries, leading to occasional outbreaks among local people and travelers. The recent outbreaks reported across 11 countries so far are atypical, as they are occurring in non-endemic countries.
-
Friday, May 20th 2022 - 09:24 UTC
WHO greenlights CanSino single-dose Covid-19 vax for emergency use
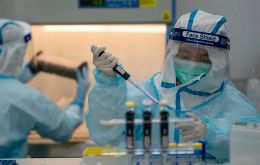
The Geneva-based World Health Organization (WHO) Thursday granted an emergency approval to the CONVIDECIA vaccine against COVID-19 developed by China's CanSino Biologics.
-
Friday, May 6th 2022 - 10:46 UTC
WHO releases “more comprehensive” COVID-19 figures

According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the number of deaths caused by COVID-19 is far larger than previously thought and has reached nearly 15 million people directly or indirectly worldwide, twice as many as initially estimated, once the WHO quantified the direct and indirect impacts of the pandemic.
-
Monday, May 2nd 2022 - 21:35 UTC
WHO concerned over resurgence of Ebola

The World Health Organization (WHO) has voiced its concern over the reappearance and subsequent spread of Ebola in the Democratic Republic of Congo, a territory formerly known as Zaire.
-
Monday, April 18th 2022 - 08:26 UTC
Brazil enters new phase in C19 crisis as cases drop significantly

Brazilian Health authorities Sunday announced a new phase in the fight against COVID-19 and the subsequent lifting of most restrictive measures adopted since 2020 to curb the spread of the disease.
-
Sunday, April 17th 2022 - 09:31 UTC
Disease outbreak in UK among children: acute hepatitis of unknown etiology

On 5 April 2022, the International Health Regulations (IHR) National Focal Point (NFP) for the United Kingdom notified WHO of 10 cases of severe acute hepatitis of unknown etiology in previously healthy young children (age range: 11 months to five-year-old) across central Scotland.
-
Tuesday, April 12th 2022 - 09:22 UTC
Paraguayan health experts warn of risk of malaria
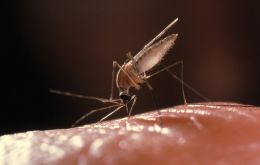
Paraguay's Health Ministry has advised that anyone returning from a country with malaria transmission and who presents fever, chills, headache, or any other discomfort should consult a physician. The disease is potentially fatal if not diagnosed and treated in time.
-
Thursday, March 24th 2022 - 09:30 UTC
WHO Ukraine report: 28 days of war, 64 verified attacks on health care, and 18 million people affected

One month of war has had a devastating impact on Ukraine’s health system, severely restricted access to services, and triggered an urgent need to treat trauma injuries and chronic conditions. Destroyed health infrastructure and disrupted chains of medical supplies now pose a grave threat to millions of people.
-
Wednesday, March 16th 2022 - 09:30 UTC
WHO says global COVID-19 infections up but deaths drop

The total number of new COVID-19 infections globally has increased by 8%, while the number of fatalities has gone down by 17%, compared to the previous seven days, the World Health Organization (WHO) announced Wednesday.
-
Thursday, March 3rd 2022 - 09:27 UTC
Mental health disorders, especially among youngsters increased 25% in first year of the pandemic, WHO report

In the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic, the global prevalence of anxiety and depression increased by a massive 25%, according to a scientific brief released by the World Health Organization (WHO). The brief also highlights who has been most affected and summarizes the effect of the pandemic on the availability of mental health services and how this has changed during the pandemic.
