MercoPress. South Atlantic News Agency
Tag: World Health Organization
-
Tuesday, June 12th 2012 - 21:50 UTC
World Health Organization classifies diesel engine exhaust as carcinogenic to humans

After a week-long meeting of international experts, the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), which is part of the World Health Organization (WHO), classified on Tuesday diesel engine exhaust as carcinogenic to humans (Group 1), based on sufficient evidence that exposure is associated with an increased risk for lung cancer.
-
Thursday, March 22nd 2012 - 21:48 UTC
World health organization supports Australia in its clash with the tobacco industry

The World Health Organization, WHO, Director-General Margaret Chan urged the world to “stand shoulder to shoulder” against the tobacco industry’s attempts to overturn Australia’s new path breaking tobacco control law.
-
Tuesday, November 29th 2011 - 02:14 UTC
Peru admits 32.477 TB cases as part of the campaign to combat the disease
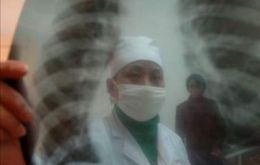
Peru has 37% of all multi-resistant tuberculosis cases in the Americas and one in four patients of the disease abandon medication in a mild stage of the disease according to the World Health Organization.
-
Monday, November 14th 2011 - 16:38 UTC
Silent killer diabetes strikes 336 million people and keeps advancing

Diabetes will strike one in 10 adults by 2030, hampering economic growth in the world's fastest-growing economies as it kills people in their most productive years, according to a report released on World’ Diabetes Day.
-
Thursday, September 22nd 2011 - 08:31 UTC
UN launches all-out attack on non-communicable diseases such as diabetes and cancer

The United Nations launched on Monday an all-out attack on non-communicable diseases (NCDs) such as cancer and diabetes with a summit meeting devoted to curbing the factors, like tobacco and alcohol use, behind the often preventable scourge that causes 63% of all deaths.
-
Thursday, September 8th 2011 - 16:16 UTC
Mosquitoes never rest: they rapidly develop resistance to insecticide treated nets

Mosquitoes can rapidly develop resistance to bed nets treated with insecticide, a new study from Senegal suggests. In recent years the nets have become a leading method of preventing malaria, especially in Africa.
-
Thursday, July 7th 2011 - 17:00 UTC
Uruguay praised by WHO as pioneer in combating the global tobacco epidemic
The World Health Organization, WHO praised Uruguay and Canada as pioneers on legislation demanding large graphic health warnings on package of tobacco, on the release of its third periodic report on the global tobacco epidemic.
-
Saturday, June 25th 2011 - 07:18 UTC
Chile among lowest for teen births in Latam, but still double the UK

Out of every 1,000 girls aged 15-19 in Chile, 51 become pregnant and give birth to a child, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). These latest figures place Chile’s percentage below pregnancy rates for all other South American countries, but still far behind nations outside the region.
-
Friday, June 3rd 2011 - 17:58 UTC
Deadly new strain of E.Coli has been detected in 12 countries, including US
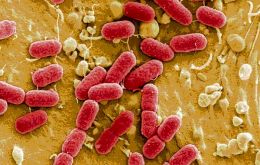
The deadly new strain of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) (E.coli) that is capable of spreading from person to person has now been detected in at least 12 countries, the World Health Organization said on Friday.
-
Thursday, April 7th 2011 - 21:57 UTC
Drug resistance becoming top global challenge, says WHO on World Health Day

Drug resistance is becoming more severe and many infections are no longer easily cured, leading to prolonged and expensive treatment and greater risk of death, warns the World Health Organization (WHO) on World Health Day.
